The slowdown of the German economy
Despite weak demand, green transition supports import growth
Published by Marzia Moccia. .
Slowdown Foreign markets Foreign market analysis
Log in to use the pretty print function and embed function.
Aren't you signed up yet?
signup!
Economic indicators confirm the slowdown of the German economy, which, according to leading international forecasters, is expected to close 2023 with a GDP decline of between -0.3% and -0.5% (source IMF and European Commission). In fact, the German economy started 2023 with a GDP decline of -0.1 percent, only to remain essentially stagnant in subsequent quarters. The country thus not only ended 2022 by posting lower growth than the EU average, but is also the only member state for which contraction is expected this year. The macroeconomic outlook for the country is thus confirmed to be complex against a backdrop of slowing global activity levels.
Foreign trade data make it possible to document the slowdown of the German economy: the following graph shows the dynamics of the country's imports, evaluated at constant prices, thus net of changes in the price level.
Fig.1 – Dynamics of German imports
(quarterly series, data at constant prices)
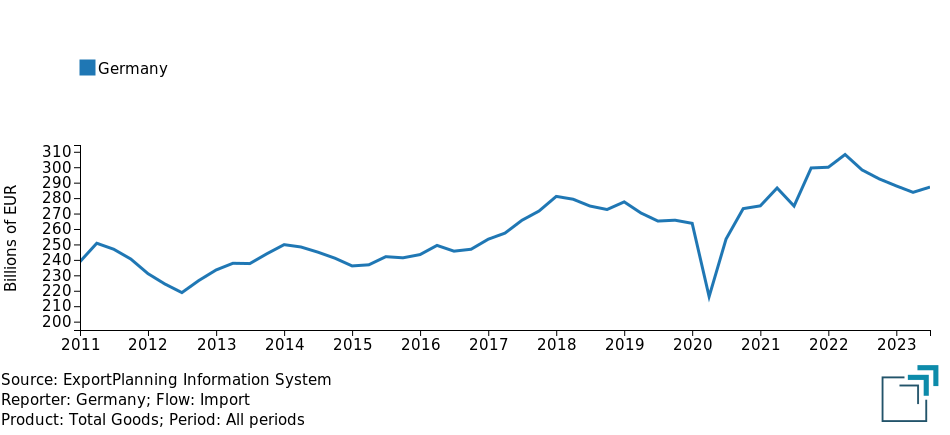
Source: ExportPlanning.
It is evident how the slowdown in German imports is documented starting in early 2022, almost coinciding with the outbreak of war in Ukraine, and has gradually intensified until the most recent quarters. Based on ExportPlanning pre-estimates, the country will end 2023 with a decline in constant prices of imports close to 6 percent. Of particular interest, however, is the signal for the third quarter of 2023, which may testify to the end of the downward dynamic that began last year, and which only the next economic information will be able to confirm.
Sectoral framework of the slowdown
Moreover, by breaking down the analysis by clusters, it is possible to derive more detailed trends with regard to the main industries.
The following graph positions the different industries of German imports, placing on the y-axis the trend change recorded between the first nine months of 2023 and the same period last year, and on the x-axis the annual change relative to 2022.
The comparison between the two was introduced in order to identify those sectors that further slowed down in 2023 compared to the previous year; the magnitude of the ball is proportional to the value of German imports in the sector.
Fig.2 - Germany: map of import dynamics by sector
(constant prices)

Source: ExportPlanning.
The decline in German imports affects several categories in product. In particular, it can be discerned:
- The slowdown in commodity imports (A1 and A2) as well as demand for various categories of intermediate goods (B). The result testifies to prudent purchasing policies on the part of enterprises, which decrease, compared to last year, the purchase in real terms of raw materials, semi-finished goods and components. This figure appears consistent with the current downturn in raw material prices, but could also be ascribed within the moderation of manufacturing activity levels;
- The downturn in demand for consumer goods most affected by the erosion of consumer purchasing power, evidenced by reductions in Fashion (E2) and Home (E3), the latter also penalized by a "physiological" context of shrinking demand after a particularly buoyant post-pandemic recovery. The only sector bucking the trend is Food&Beverage(E0), which in 2023 substantially rebounded from the "timid" results of the previous year;
- The greater resilience of investment assets (F) which, with the exception of ICT Equipment (F1) testify to substantial resilience, discernible in both last year's and current data;
- Finally, mention must be made of the industries that are driving German demand for goods, closely related to the new sustainability challenge. The sectors that are bucking the trend are in fact Automotive (F3 and D3), thanks to the strong push of electronics, and Electrical Engineering (D4), given the increasing relevance of the sector within electrification and energy efficiency processes.
In line with economic agents' expectations and analysts' growth estimates, foreign trade data document the difficulties of the German economy.
According to a number of commentators, there are conjunctural and structural circumstances that have impacted the country's growth. First, mention must be made of the energy shock, linked to the Russian invasion of Ukraine and Germany's high dependence on gas imported from Russia, which made the country's industry more vulnerable to negative effects in the most critical months of last year. The difficulties of the entire "traditional" automotive supply chain, which has been affected by profound and significant changes toward the world of electrics, must also be emphasized. It is no coincidence that German Automotive exports never recovered - at constant prices - to 2018 values, following the Dieselgate scandal and related regulations.
Fig.3 – Dynamics of German automotive exports
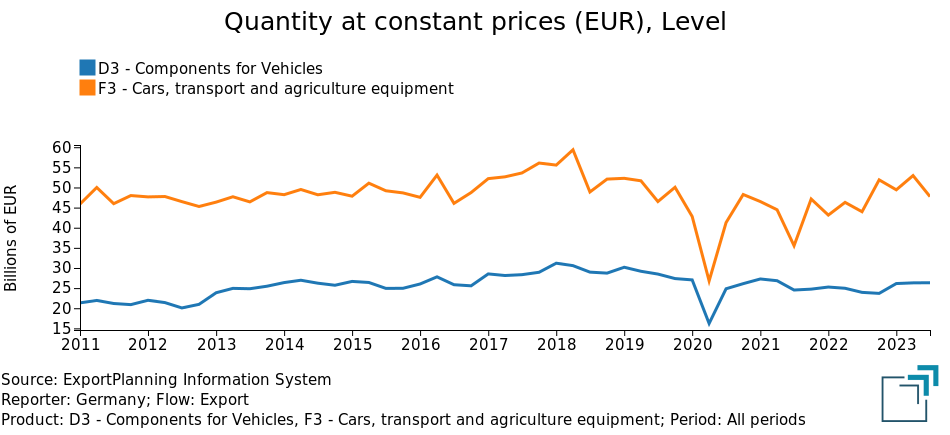
Source: ExportPlanning.
Also weighing heavily is the Chinese slowdown: in fact, Germany is the European economy most interconnected with the Dragon country, suffering most from the relative difficulties.
Fig.4 – Germany-China trade exchange
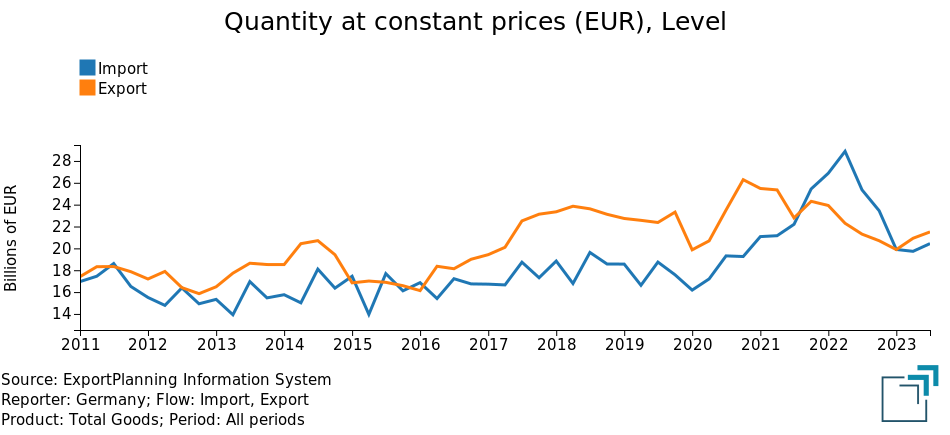
Source: ExportPlanning.
What signs are discernible in the most recent quarters?
Against a picture that is certainly complex for one of the main destination markets for made in Italy, the outlook nevertheless appears to be stabilizing.
The most recent publication of the Business Climate Ifo Index, which measures German economic agents' perceptions of the current and six-month economic situation, showed encouraging signs. In fact, this index, based on the combination of three qualitative indicators (order level, inventory change and production expectations), recorded the third increase in terms of local agents' expectations; a result that has been interpreted as the possible end of the contractionary phase toward one of relative stagnation.
Fig.5 – Germany: Business Climate Ifo Index
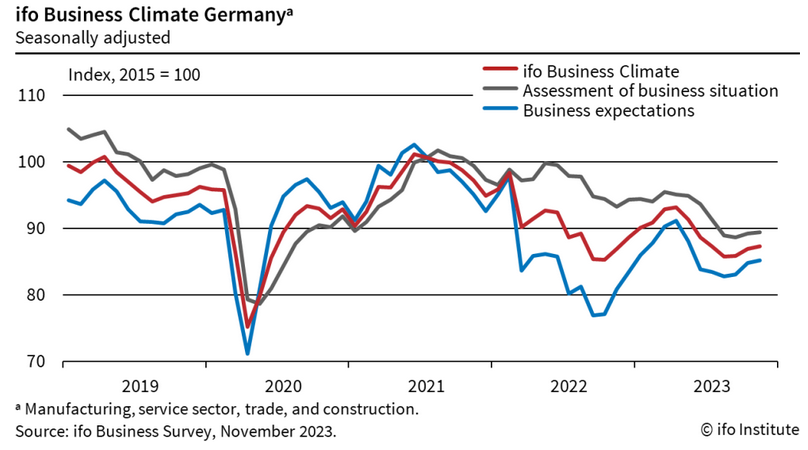
It seems more necessary than ever for exporting companies to enhance the role of information in the formulation of the 2024 budget, in order to constantly monitor the major phenomena in place and thus efficiently allocate the marketing resources.


